Dr. Claudia Pinter is finding the advanced technologies in Spark Aligners and Approver Software are allowing her to offer a greater range of esthetic treatments in her orthodontic practice.

Dr. Claudia Pinter discusses an essential tool in her orthodontic practice
As a young orthodontist starting my career in Vienna, Austria — a city with many well-established colleagues — my dream was to serve patients with high esthetic demands. At that time, aligners were considered suitable only for mild malocclusions. However, after attending courses on Spark™ Clear Aligners, I realized that by incorporating the principles of orthodontic biomechanics into aligner treatment plans, the possibilities of what we can achieve with “a piece of plastic” seemed limitless.
The Spark Approver Software became an essential tool in my practice, offering a wide range of features for designing predictable treatment outcomes. The ability to visualize simulated root positions proved invaluable for planning the biomechanics to achieve the desired tooth movement.
Having previously used other aligner brands, I was pleasantly surprised when patients reported greater comfort and less staining with Spark Aligners. This improved patient experience likely contributed to more compliance with wear time, which, in turn, led to better clinical results.
My plan to create a niche offering of esthetic orthodontic treatments with aligners that achieve the same level of excellence as traditional braces was a success.
Focusing on adult treatments, it was deeply rewarding to see my patients’ newfound smiles and confidence.
In this article, we will explore how advanced technologies like Spark Clear Aligners and Approver Software, as well as the visualization of simulated roots, have revolutionized orthodontic treatment planning.
Case 1
A 17-year-old female patient presented for a second opinion on achieving a more harmonious smile. A previous dentist had suggested veneers for teeth 3-3 in the upper arch, but the patient was uncomfortable with this invasive approach. The intraoral examination revealed crowding, a deep bite, and a dental Class I relationship on the right side, with a full Class II on the left. The panoramic X-ray indicated the absence of a third molar in the second quadrant.

The treatment objectives were to improve smile harmony, align teeth, and establish functional occlusion.
The treatment plan included sequential distalization in the second quadrant to achieve a Class I dental relationship and a symmetrical upper arch. Spaces of 0.5 mm were planned mesially and distally to the upper laterals for composite buildups, further enhancing tooth proportions. Heavy Class II elastics (full-time wear) were employed to reinforce anchorage during sequential distalization.
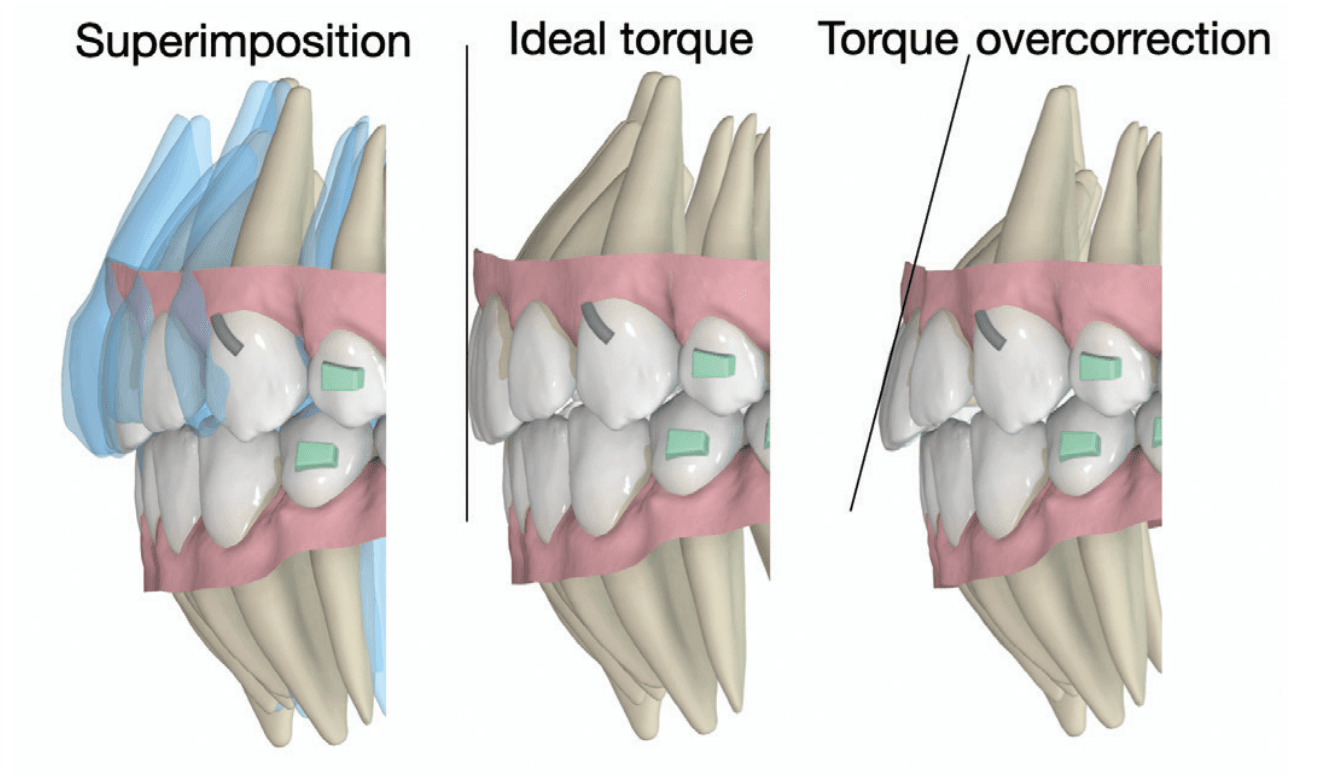
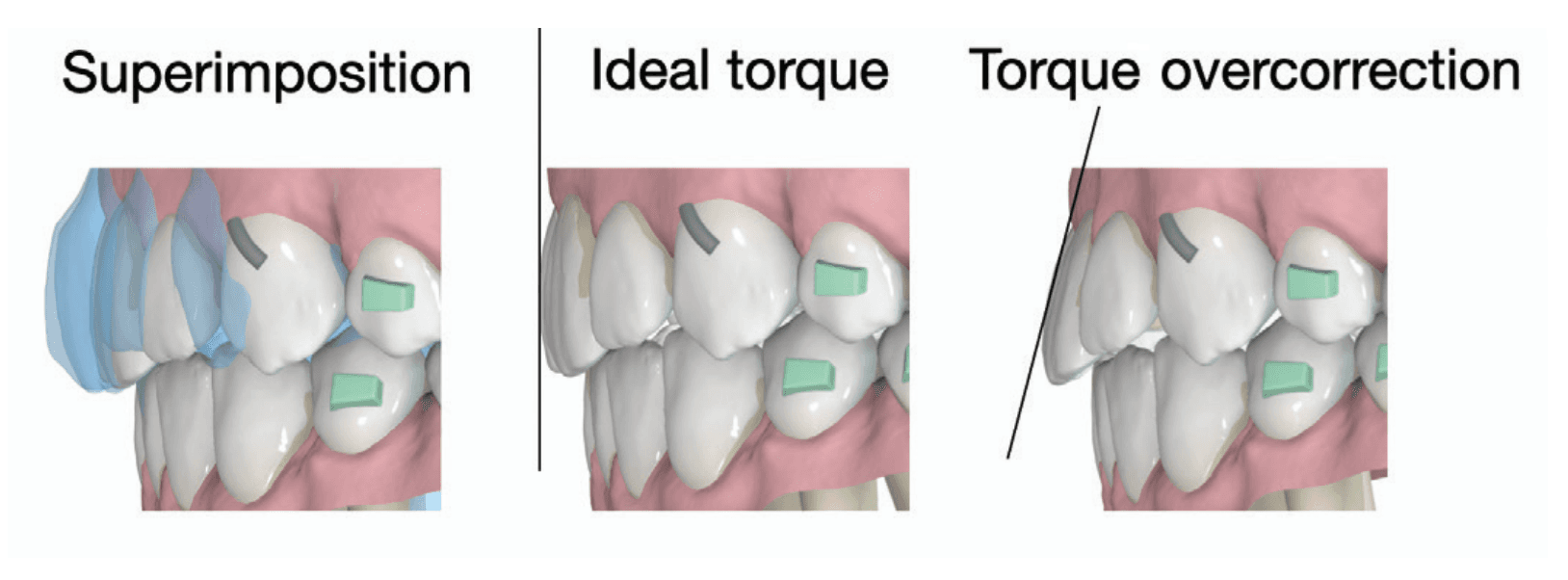
An additional 10° of lingual root torque was prescribed for the upper incisors to counteract the retroclination of upper incisors, a potential side effect of Class II elastics.
Technician instructions: Sequential distalization of 50% in the second quadrant, with 10° additional lingual root torque for upper incisors (2-2).
The additional lingual root torque was essential to prevent retroclined incisors, which could lead to anterior pre-contacts and potentially result in a posterior open bite.
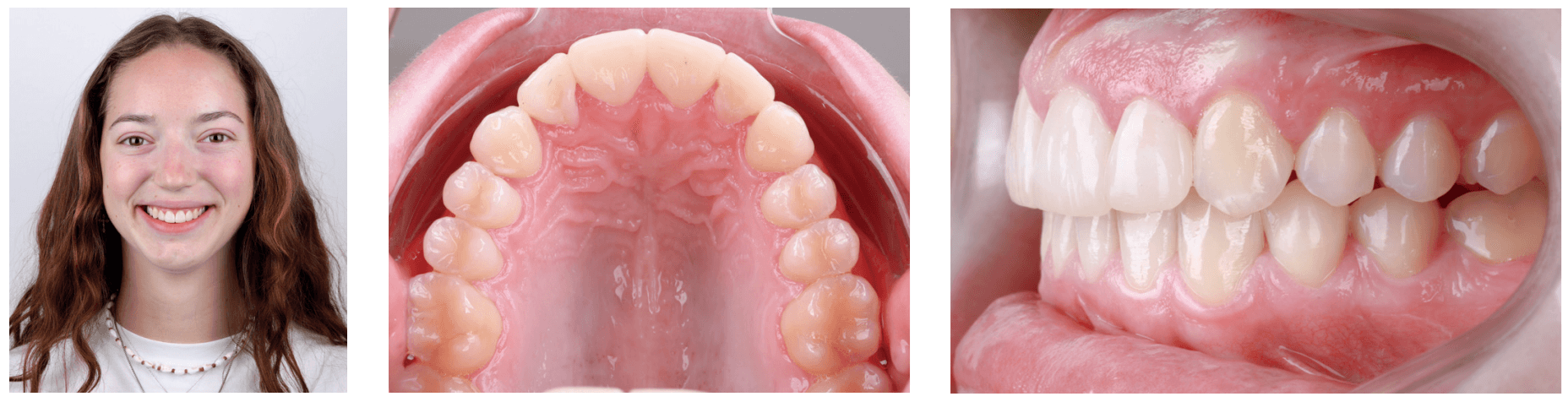
Results
A dental Class I relationship was achieved on the right side, with maintained torque in the upper incisors, and the patient expressed satisfaction with her improved smile harmony.
Case 2
A 32-year-old female patient presented with a desire to enhance her smile. She exhibited large buccal corridors and crowding in the incisors. Intraorally, a deep bite and retroclined upper and lower incisors contributed to a steep interincisal angle.
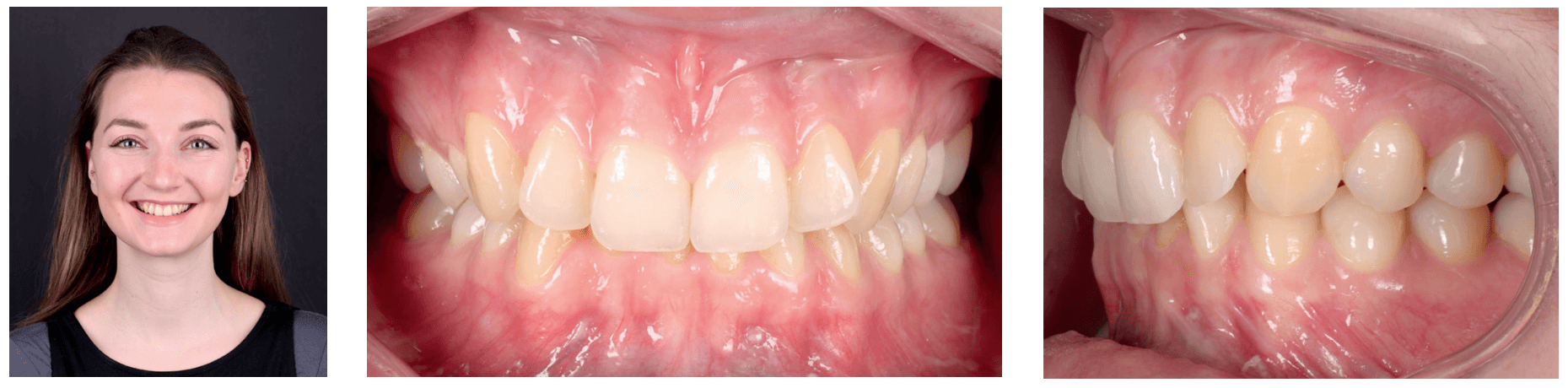
The treatment goals included achieving parallelism of posterior tooth torque, broadening the smile, creating a smile arc with a gradual front-to-back transition, and centering the midline through distalization of the second quadrant, supported by Class II elastics.
A specific challenge was posed by the retroclined incisors, which required correction of torque while achieving retraction.
Instructions to the Spark Approver Designer: Sequential distalization of 50%, with an additional 10° root torque for upper 2-2. Place a cut in UR4 and a button cutout on LL7.
Removing the upper left wisdom tooth could have facilitated distalization; however, the patient preferred to proceed without its removal.
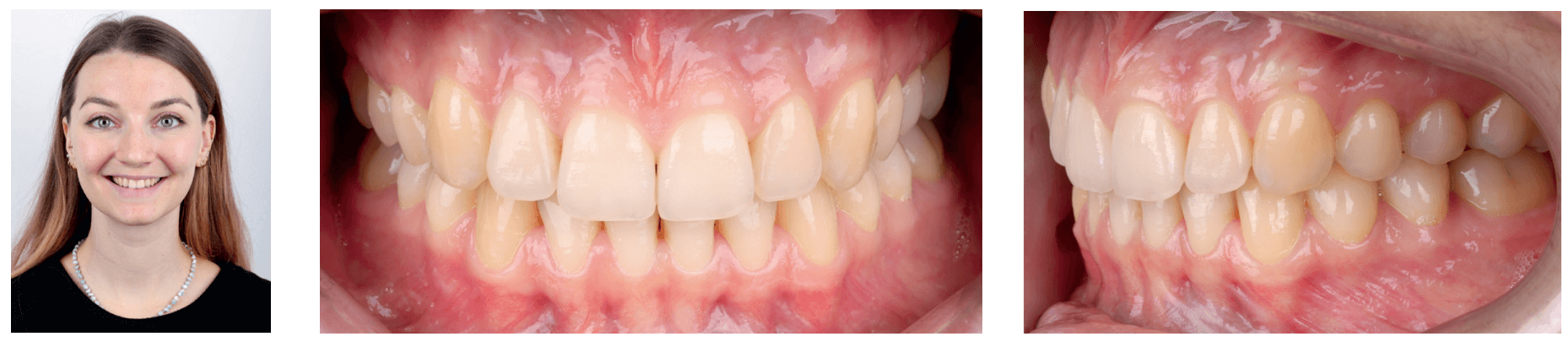
Final results
A dental Class I relationship was achieved, with adequate overbite and overjet. Smile evaluation demonstrated a broad smile with gradual front-to-back transition, parallelism of posterior tooth torque, and proper posterior occlusion.
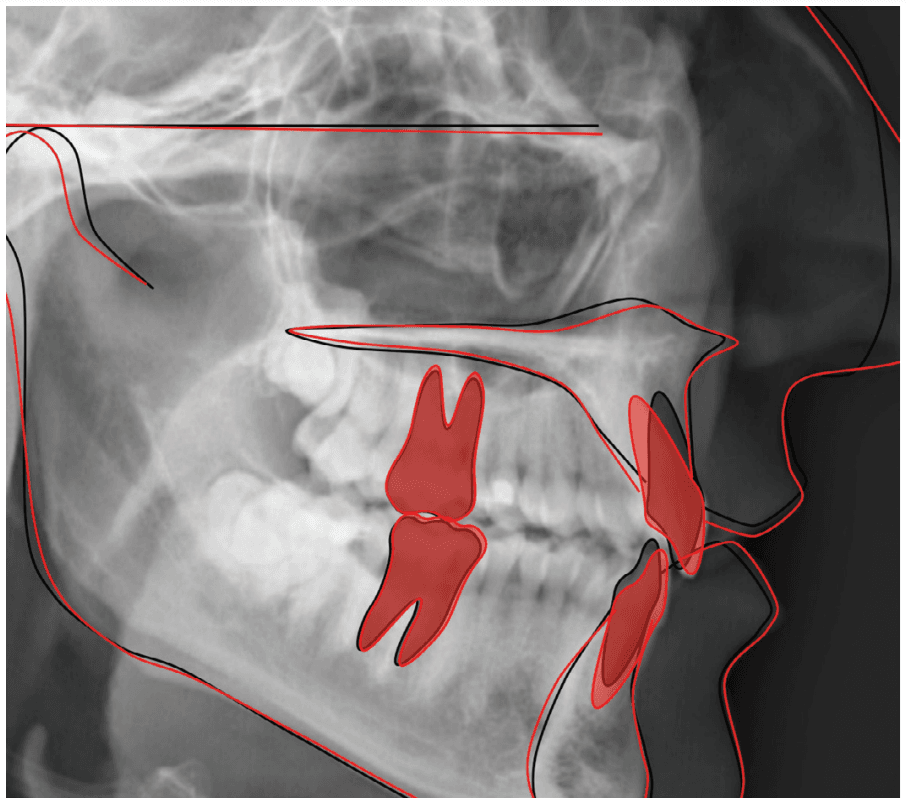
Discussion
Aligners are widely recognized for their efficiency in tipping crowns but are often regarded as less effective in achieving root torque. These cases illustrate that Spark Aligners can successfully deliver lingual root torque in the upper incisors. Root torque is critical for an optimal interincisal angle, proper anterior guidance, and improved esthetics. Unlike tipping movements, clinicians are advised to plan an overcorrection of approximately 10° for cases requiring lingual root torque to prevent retroclined incisors at treatment end.
Without root visualization, achieving accurate lingual root torque can be challenging. Spark Approver Software provides root visualization capabilities, allowing clinicians to accurately assess root movements required to meet desired outcomes. This feature enables simulated root visualization even without a CBCT submission.
To read about some upgrades to Spark Aligners and Approver Software, click here: https://orthopracticeus.com/industry-news/ormco-corporation-announces-upgrades-to-its-approver-software-for-the-spark-clear-aligner-system-as-well-as-a-more-intuitive-and-user-friendly-case-management-portal/
Stay Relevant With Orthodontic Practice US
Join our email list for CE courses and webinars, articles and mores


