Erupting impacted cuspids can be challenging, so Dr. Lloyd Taylor shows a step-by-step method, using Gold Mesh Pad for efficient and controlled direction.
Dr. Lloyd Taylor illustrates a technique for impacted cuspids
Surgical attachments to impacted teeth requiring eruption into the dental arch have gone through a long and tortuous evolution. The majority of the procedures are performed on impacted cuspids since they are often the last teeth to erupt into the dental arch. The following describes the development leading to Gold Mesh Pads:

- Lasso made of .012″ wire was looped around the cuspid cervix after bone and soft tissue were removed. The wires of the lasso were twisted tightly to form a loop for elastic traction. Many of these lassoed cuspids were later extracted because of ankylosis due to the removal of some periodontal membrane resulting in alveolar bone fusing to root cementum.
- Tunnel was cut through bone to the uncovered cuspid. A crown form was sutured in the tunnel while it epithelialized. These teeth eventually erupted after many years, which enormously extended orthodontic treatment time.
- Pin allowed access to be cut through enamel to dentin for a tiny drill to prepare a hole to screw in an eyelet pin. The eyelet was tied for eruption. Unfortunately, the damage to the tooth crown was difficult to repair, eyelets were difficult to tie, and often pulpal damage occurred.
- Acid etch bonded brackets and buttons, eliminating crown damage and ankylosis, but attachments were often lost requiring repeated surgeries. It was difficult to light-cure adhesives under solid attachments.
- Gold Mesh Pads with swivel eye-lets and gold chain have become the standard treatment for the eruption of impacted teeth. With proper bonding and surgical technique coupled with gentle elastic force, teeth erupt efficiently and with controlled direction.
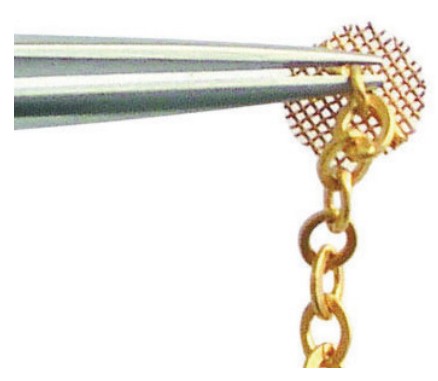


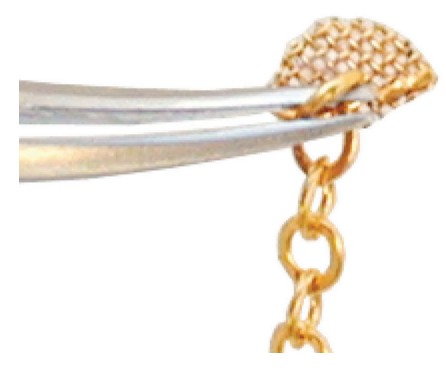
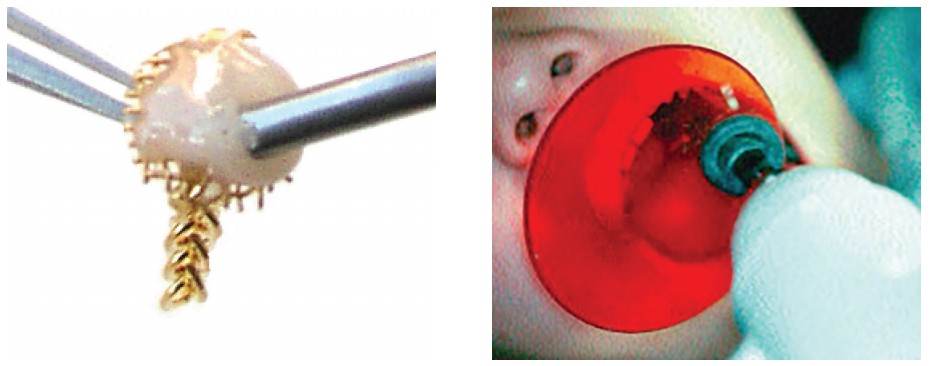

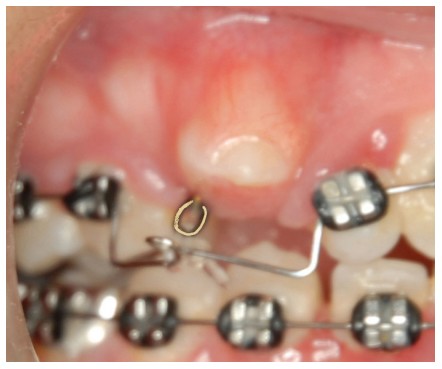
After discovering the Gold Mesh Pad, check out Dr. Taylor’s step-by-step on the Tie-On Rotation Wedge for orthodontic finishing.
https://orthopracticeus.com/tie-on-rotation-wedge-torw-for-perfect-orthodontic-finishing-part-2/
Stay Relevant With Orthodontic Practice US
Join our email list for CE courses and webinars, articles and mores

 Lloyd R. Taylor, DDS, received his DDS degree from Fairleigh Dickinson Dental School. He first completed a 3-year residency in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Anesthesiology and was Chief Resident at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine/Jacobi Hospital in New York City. Dr. Taylor then completed a 3-year Fellowship in Orthodontics at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine. He also completed an additional 3-year Fellowship in Orthodontic Teaching and Research at the Forsyth (Harvard) Dental Center. Dr. Taylor has practiced both Oral Surgery and Orthodontics in North Hollywood, California, for more than 50 years.
Lloyd R. Taylor, DDS, received his DDS degree from Fairleigh Dickinson Dental School. He first completed a 3-year residency in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Anesthesiology and was Chief Resident at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine/Jacobi Hospital in New York City. Dr. Taylor then completed a 3-year Fellowship in Orthodontics at the Harvard School of Dental Medicine. He also completed an additional 3-year Fellowship in Orthodontic Teaching and Research at the Forsyth (Harvard) Dental Center. Dr. Taylor has practiced both Oral Surgery and Orthodontics in North Hollywood, California, for more than 50 years.
